Balloon angioplasty expands narrowed blood vessels. This page explains how this procedure will help your child with a heart condition.
What is balloon angioplasty?
Balloon angioplasty, also known as balloon dilation, is a procedure to expand narrowed blood vessels and improve blood flow. It is used in conditions such as:
- coarctation of the aorta
- pulmonary stenosis
- narrowing of veins such as the superior or inferior vena cava
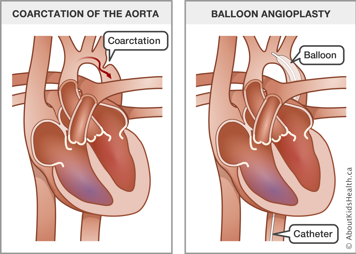
How is balloon angioplasty carried out?
The procedure is performed while your child is under a general anaesthetic. This means that your child will be asleep during the procedure.
During the catheterization, the doctor threads a special catheter through your child’s blood vessels to the narrowed area. The team takes X-ray pictures and measurements of the coarctation. Then the team threads a deflated balloon on the tip of the catheter to the area of the coarctation. The balloon is then inflated to open up the narrowed area. Sometimes a second larger balloon is used to dilate the area further.
Sometimes the doctor may choose to put in a stent. A stent is a small metal tube made of stainless steel or another type of metal. The stent helps support the walls of the blood vessel to keep it open.
After the coarctation is opened up, the team takes a second set of pictures and measurements. The doctor then takes out the balloons and catheters and covers the cuts on your child’s legs with a bandage.
