At the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- identify important components in performing chest compressions
- describe how to landmark for chest compressions based on the child’s age
It is important to know how to perform chest compressions safely but effectively. This page provides guidelines on performing chest compressions, but it does not replace hands-on CPR training from your child’s health-care team. It is recommended to do yearly CPR re-certifications to ensure that your skills are up to date.
Guidelines for chest compressions
The general guideline for chest compressions is 30 compressions, at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions a minute, followed by two breaths. This is known as a compression-to-breath ratio of 30:2.
When performing compressions, it is important that you do the following:
- Ensure you do the compressions on a firm flat surface. Move to the ground if possible.
- Ensure that you push down hard enough, based on the child’s age (see below).
- Ensure that you are pushing fast enough at a rate of 100 to 120 beats per minute.
- Ensure that you allow the chest to fully come back to its original position (recoil) after each compression. This allows the heart to effectively refill after each compression.
- Minimize interruptions when doing chest compressions. After giving breaths, go back to the chest right away.
Depth for chest compressions
The depth of the chest compressions depends on whether your child is considered an infant, a child or an older child or teenager. In infants and children, the compression depth should be at least ⅓ the depth of the child's chest.
Chest compression guidelines by age
- Infant = under one year of age
- Child = one year to puberty
- Older child/teen = from the start of puberty* onwards
*In girls, puberty starts when breasts start to develop. In boys, puberty starts when underarm hair starts to appear.
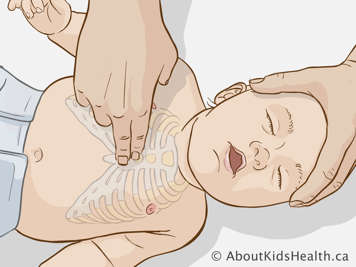
Chest compressions for infants (under one year of age)
- The compression depth for an infant is 4 centimetres (1.5 inches).
- Place your two fingers on the centre of the chest just below the nipple line. Give 30 quick chest compressions followed by two breaths. Repeat with a compression-to-breath ratio of 30:2.
Chest compressions for children (one year to puberty)
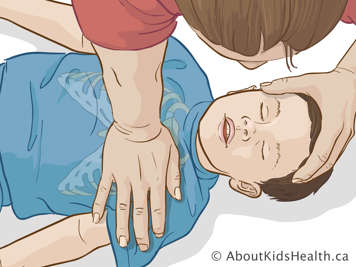
- The compression depth for a child is about 5 centimetres (2 inches) or at least ⅓ the depth of the chest size.
- Place the heel of your hand on lower half of breastbone and give them 30 quick chest compressions followed by two breaths. Repeat with a compression-to-breath ratio of 30:2.
If you are not compressing deep enough, you may use two hands. Do so by placing one hand on top of the other hand.
Chest compressions for older children and teens (from puberty onwards)
- The compression depth for this age group is at least 5 centimetres (2 inches) but no more than 6 centimetres (2.5 inches).
- Place the heel of one hand over the lower half of your child's breastbone. Place the second hand on top of first. Give them 30 quick chest compressions followed by two breaths. Repeat with a compression-to-breath ratio of 30:2.