Most babies with transposition of the great arteries (TGA) will need to undergo a procedure called balloon atrial septostomy.
What is balloon atrial septostomy and why is it done?
In TGA, because the aorta and the pulmonary arteries are switched, there are two disconnected blood circulations: the oxygen-rich ("red") blood flows only to the lungs while the oxygen-poor ("blue") blood circulates through the heart and the body.
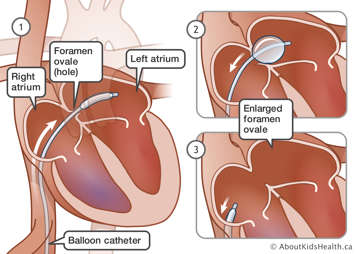
A balloon atrial septostomy enlarges a naturally occurring hole (called the foramen ovale) between the left and right atria. Because blood from both sides of the heart can now mix together, oxygen can be delivered to the rest of the body.
This is only a temporary measure until a baby is ready for a surgery called the arterial switch operation, which will create a normal circulation of blood in the body.

How is balloon atrial septostomy done?
This procedure is done by a cardiologist who specializes in catheter procedures, often assisted by a cardiology fellow. The balloon atrial septostomy is usually performed in the baby’s room, at the bedside, in the cardiac critical care unit (CCCU). The health-care team uses images produced by ultrasounds to guide the procedure.
However, in some cases, if the echocardiogram hints at a more difficult procedure, the balloon atrial septostomy may be carried out in in a special procedure room called the cardiac catheterization laboratory.
A special catheter that has a balloon attached to its tip is introduced into the body through a blood vessel in the groin or belly button. Once the catheter is pushed all the way to the left atrium of the heart, the balloon tip is inflated and pulled into the right atrium of the heart. By gently tearing some of the muscle that divides these two atria, the small foramen ovale becomes bigger.
The balloon is then deflated and the catheter is removed from the body. If the catheter was pushed through the groin, your baby will have a small incision (cut) covered with a bandage.
In some cases, there is no foramen ovale. Your child’s health-care team may judge it necessary to create one with a special catheter in addition to the balloon. This special procedure will be performed in the cardiac catheterization laboratory where different equipment and imaging tools may be required.
Your baby will be under anesthesia for the procedure.
Risks of balloon atrial septostomy
A balloon atrial septostomy is considered a low-risk procedure. The risks may depend on your baby’s overall health. Risks include:
- bruising at the groin
- blood clot
- infection
- bleeding
- arrhythmia (arrhythmia refers to a fast, slow, or irregular heartbeat)
- stroke with TGA
Giving consent before a balloon atrial septostomy
One of the heart specialists will explain the procedure to you. The anesthesiologist will also speak to you. You are encouraged to ask questions so that you understand the procedure. You will then be asked to sign a consent form before the procedure.
Pre-procedure
Newborns must be fasting (not be fed) before the procedure is done. It is possible to save breastmilk to feed your baby later.
If your newborn is not already on a breathing machine, the medical team looking after your baby will arrange for this so that the procedure can be done safely.
Pain
Your baby will receive pain medication and sedation before and during the procedure.
After the procedure
After the procedure, your baby will be allowed to wake up and slowly come off of the breathing machine if they are breathing well on their own.
If the oxygen levels are good, your child’s health-care team will try to stop the prostaglandin medicine.