Diabetes is a life-long condition that occurs when the body is not able to use and store sugar for energy.
Sugar in the bloodstream is called glucose, and it comes from the carbohydrates in the foods we eat. Our body uses energy from glucose without us even realizing it. We need energy to:
- produce body heat
- make our muscles work, our hearts beat, our lungs breathe, our brains think
- allow the growth, renewal, and repair of the billions of cells that make up our bodies.
In order to use glucose (sugar) for energy, our bodies require a hormone called insulin. Diabetes occurs when the body is not able to use and store sugar for energy because the pancreas:
- does not make insulin
- makes too little insulin
- cannot respond to the insulin that is made.
What does insulin do?
Insulin is made in the pancreas. The pancreas is an organ that sits behind the stomach. There are special cells in the pancreas, known as beta cells, which make insulin. Beta cells are found in areas of tissue called the islets of Langerhans.
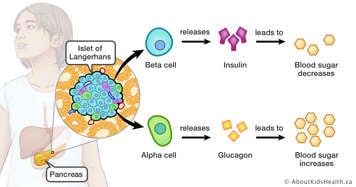
This animation shows how sugar is released in the body and turned into energy with the help of insulin. The animation is supplemental and repeats information from the text on this page.
Insulin is a hormone. A hormone is a chemical "messenger" that travels through the blood to help organs and tissues carry out their proper functions. Insulin travels through the body and opens cell channels to allow sugar from the blood to enter the cell so the cell can use the sugar for energy. Insulin also allows sugar to be stored in tissues, such as liver and muscle, so that it can be released later for energy in areas where it is needed such as the brain and heart.
If there is not enough insulin, cells are unable to use the sugar to make energy. The unused sugar builds up in the blood and is passed out of the body in urine (pee).
If the sugar cannot be used, the body looks for other sources of energy, such as fat. Fat break down produces ketones; they can be harmful.
Energy from food
In order for us to supply our bodies with energy, we must eat food. As the food we eat is broken down (digested) in the stomach and small intestine, nutrients are released and absorbed into the bloodstream, and carried to all parts of the body.
There are three major nutrients: carbohydrates, proteins and fats. All three are necessary for survival; however, it is carbohydrates that are used for energy by the cells after they break down into sugar.
Food does not need to be sweet to turn into sugar; some vegetables, bread, and potatoes all become sugar when they are broken down in the body.
A steady stream of sugar is necessary to supply the brain, nerves, and all the other systems in the body (such as the circulatory system, which allows our hearts to beat).
Sugar also provides extra bursts of energy when we need it during school, at work, or while we are playing sports.
Whenever we eat food containing carbohydrates, sugar enters the bloodstream. In people without diabetes, the pancreas responds by releasing the right amount of insulin into the blood. This naturally prevents blood sugar level from getting too high or too low and provides the cells with just enough energy to complete its required tasks.
Patients with diabetes either produce no insulin or not enough insulin or their body becomes resistant so it does not respond to the insulin that is produced; as a result, sugar builds up in the bloodstream after meals.
If the body does not produce insulin naturally, then patients need to take insulin. Insulin can only be given by injection.
If the body is resistant to insulin and cannot make enough insulin to overcome this resistance, then patients need to control the types of food that they eat to reduce the amount of insulin required to function normally. This is usually achieved through diet and exercise. Sometimes specific oral medications (pills) can help the body make more insulin or respond better to insulin (increase insulin sensitivity). These pills do not contain insulin.
The different types of diabetes are described in the following sections.