What is deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is caused by a blood clot (thrombus) that occurs in the deep venous system. Deep veins are located within the muscles and are very important as they transport the blood back to the heart with the assistance of both vein valves and muscle contractions. Valves are found throughout the veins, especially in the legs, and help push the blood from the periphery of the body through the veins toward the heart. Hence, valves prevent backward blood flow, away from the heart. DVT can occur in the deep veins of the legs or arms. The blood clot fills the interior of the vein, obstructing the blood flow and causing several complications.
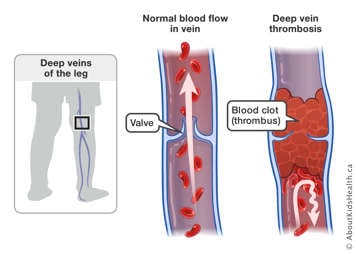
What are blood clots?
Clotting factors are proteins in the blood that help to stop cuts and wounds from bleeding. Platelets, one of main elements in blood, work together with the clotting factors to stop bleeding by creating blood clots. Blood clots are clumps of blood, including clotting factors and platelets, which harden over time to stop wounds from bleeding.
Signs and symptoms of DVT
DVTs located in the arms or the legs can be accompanied by limb swelling, pain, and changes in the color of the skin (red or bluish color).
Causes of DVT
DVTs are less common in children than in adults. Until recently, there was very little information describing the risk factors for DVT in children. However, some of the following risk factors found in adults are thought to also affect children who have DVT. Recent work by international research groups is helping to clarify risk factors for the development of DVT in children. Children admitted to a pediatric hospital are at the highest risk for thrombosis, which is largely due to the use of catheters or to their underlying health problem.
Blood vessel damage
DVT can be seen in children that have a central venous line or catheter that is used to give medications inside the deep venous system. In most cases, micro damage to the vein caused by the line causes platelets and clotting factors to start a clot. Blood also flows more slowly around the line. As a result, blood cells stick to the clot causing it to grow.
Anatomic variants and exercise-induced DVT
Changes in the anatomy or arrangement of blood vessels or the muscles close to blood vessels can lead to DVT in teens and young adults. These changes may cause tight corners within the blood vessels, which slow down the blood flow. Some anatomic changes can cause trauma to blood vessels during repetitive and intense exercise, resulting in blood clots.
Medical and genetic conditions
Certain infectious conditions (such as osteomyelitis) and inflammatory conditions (such as antiphosphospholipid syndrome) can also trigger the clotting system. These conditions provide a false signal similar to the one that happens when an injury occurs, therefore increasing the risk of clot in the deep veins.
Similarly, conditions such as vasculitis (inflammation of the blood vessels) and some medications, such as chemotherapy, can lead to DVT.
In addition to medical conditions or medications, blood clots may appear in children whose blood clotting system produces clots more easily than those of other children. For example, some children may inherit genes from one or both of their parents that can increase their risk for developing a blood clot. In some cases, there can be a significant family history of clots, which present themselves in the form of DVT, heart attacks (myocardial infarction), strokes, or clots in the lungs (pulmonary embolism), and multiple miscarriages from clots in the placenta.
Age
As a person ages, the walls of their veins become less elastic and more susceptible to venous problems. Similarly, the circulating clotting factors rise with age, making clotting more common in older adults than in neonates and children.
Immobility
If a person is immobile (confined to a bed, unable to walk or spending large parts of the day in a bed or chair), the skeletal-muscle pumps, which help blood in the deep veins to return to the heart, are at rest. This leads to a slow blood flow inside of the deep veins of both legs, increasing the risk of blood clots.
In adults, there is a small risk of thrombosis when being relatively immobile when travelling by plane, train, car, bus or boat. The risk for DVT while travelling is higher for people affected by one or more of the other risk factors listed.
Obesity
Obesity is associated with conditions that may increase the risk of DVT.
Dehydration
When the body is dehydrated, the blood has a tendency to thicken, which increases the risk for developing DVT.
Hormone therapy
Birth control pills, patches or rings that contain estrogen increase the risk of DVT, particularly during the first year of usage.
Diagnosis of DVT
Blood clots are suspected when the obstruction of a vein results in problems. For example, a leg with a blood clot in the deep veins becomes swollen, red, and painful. To confirm this suspicion, blood clots are usually diagnosed with an ultrasound. An ultrasound is a medical test that uses sound waves to obtain images of structures inside the body, such as blood flow through a vein. In some cases, other imaging tests may be required. For example, to diagnose a clot in the lungs, a tomography (a special type of X-ray of the lungs) or a ventilation-perfusion scan (which measures the air and blood supply to the lungs) might be required.
In addition, children usually undergo blood tests when a clot is suspected to make sure it would be safe to start treatment, if required.
The thrombosis team is responsible for diagnosis, initial management, and follow-up. The team will also coordinate your child’s future follow-up in the thrombosis clinic, where the blood clot will continue to be monitored over time.
Treatment of DVT
There are four different treatments that can be done when a child is diagnosed with DVT.
Wait and watch
In some cases, your child’s doctor may decide not to treat the clot right away. This could happen if the clot is old, or if your child’s doctor determines that the risk of treatment outweighs the benefit. In those situations, it is reasonable not to give medications to help with the clot and to monitor your child closely. Your child’s doctor may take new imaging scans to evaluate if the clot is growing in the absence of treatment.
Anticoagulant drugs
Anticoagulants (blood thinners) can be prescribed to treat DVT. This treatment helps stabilize the clot, preventing growth and new clot formation so the body can use its own natural mechanisms to break down the clot.
These drugs include the anticoagulants from the family named heparinoids (standard heparin,
tinzaparin, dalteparin, reviparin, nadroparin and
enoxaparin), ultralow heparin (fondaparinux), or the family named oral
vitamin K antagonists (OVKA;
warfarin, acenocumarol, phenprocoumon). Heparinoids are administered through the veins (standard heparin) or as injections through the skin (subcutaneous injections; tinzaparin, dalteparin, reviparin, nadroparin, enoxaparin). Fondaparinux is also administered subcutaneously, whereas OVKA are administered by mouth. In all cases, anticoagulation medications in children due to a DVT are usually given for three months. Exceptions may occur for very young children (newborns and infants; six-week duration may be considered), or for patients that have a long-lasting thrombosis risk factor (duration longer than three months).
Thrombolysis
Thrombolysis is the process by which the clot is broken down either mechanically, or with the aid of a “clot-busting” medication. This option is considered only when there is an extensive blood clot, or when there is loss of blood supply to an organ or limb because of the clot’s presence, causing a risk of organ or limb loss.
Thrombolysis can be given in the hospital as an infusion, where the patient will be closely monitored. Thrombolysis may also be performed by an interventional radiologist using image guidance. The interventional radiologist uses a catheter to break up the blood clot and monitors the procedure with X-ray imaging.
Surgery
In rare cases, surgery will be performed to remove the blood clot. Surgery as a treatment is rare and usually only used in emergency situations.
Prevention of blood clots and DVT
The best way to prevent blood clots and DVT is to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Exercise: Going on daily walks or participating in other aerobic exercises such as swimming can improve blood circulation and prevent new clots from forming.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water reduces risks of blood clotting by maintaining a liquefied consistency in the blood. Avoid substances that dehydrate the body, such as caffeine and alcohol.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking increases the likelihood of platelets sticking together and damages the lining of the blood vessels. If you or another family member smokes, and your child is at risk for blood clots, make sure you keep your home, vehicle and anywhere else your child will be, a smoke-free environment.
Complications of blood clots and DVT
Fresh clots like to grow within the deep venous system. Occasionally, a smaller portion of the clot breaks off and is transported into different locations of the body, depending on where it originated. Sometimes, the fragmented blood clot travels all the way to the lungs. When this happens, it is called a pulmonary embolism.
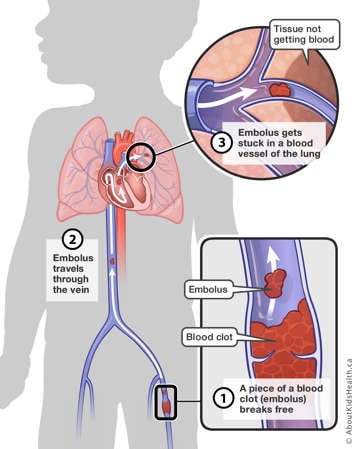
Very rarely, when a small hole in the heart is present, the blood flow of the right side of the heart may travel to the left side. This allows the blood clot to enter the left side of the heart, which provides blood to the brain. This increases the risk of a paradoxical embolism or stroke.
Other potential complications of clots are recurrence (when the clot comes back or there is a new clot somewhere else) and post-thrombotic syndrome.
It is highly unlikely that part of a blood clot left in the vessel after some time will travel to a new location in the body. After about six weeks, the clot starts to become “old” and calcifies, becoming part of the vessel. At this point the clot is considered to be stable and unlikely to cause further damage.
At SickKids
The thrombosis team at SickKids includes a nurse practitioner (NP), staff physicians, thrombosis fellows, and research staff.
If you are a SickKids patient, you will attend follow-up appointments in the thrombosis out-patient clinic, open Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays.
For SickKids patients, please see below for contact information in non-urgent and urgent situations:
- For non-urgent clinical matters, contact the Nurse Practitioner at: 416-813-8514
- For appointment clarification or rescheduling, contact the Thrombosis Clinic Coordinator at: 416-813-5453 extension 2
- For after-hours clinical emergencies, contact the Thrombosis Fellow on-call at: 416-813-7500
For more information on thrombosis, post-thrombotic syndrome and the management of these conditions, please visit the
Thrombosis Learning Hub.