What is prothrombin gene mutation
Prothrombin gene mutation is a blood clotting disorder. Prothrombin is a clotting factor. Clotting factors are proteins in the blood that help to stop cuts and wounds from bleeding. Platelets, one of the main elements in blood, work together with the clotting factors to stop bleeding by creating blood clots. Blood clots are clumps of blood, including clotting factors and platelets, which harden over time to stop wounds from bleeding. Once the bleeding is controlled, the blood clot stops growing.
Prothrombin mutation results in overproduction of prothrombin, which slightly increases the risk of developing blood clots in the veins.
Prothrombin gene mutation affects approximately 2% of Caucasians and is infrequent in people of Asian or African descent.
What are the signs and symptoms of prothrombin gene mutation?
A prothrombin gene mutation itself does not cause any signs and symptoms. However, if your child develops a blood clot, they will have symptoms related to the clot. Signs and symptoms will depend on where in the body the blood clot is.
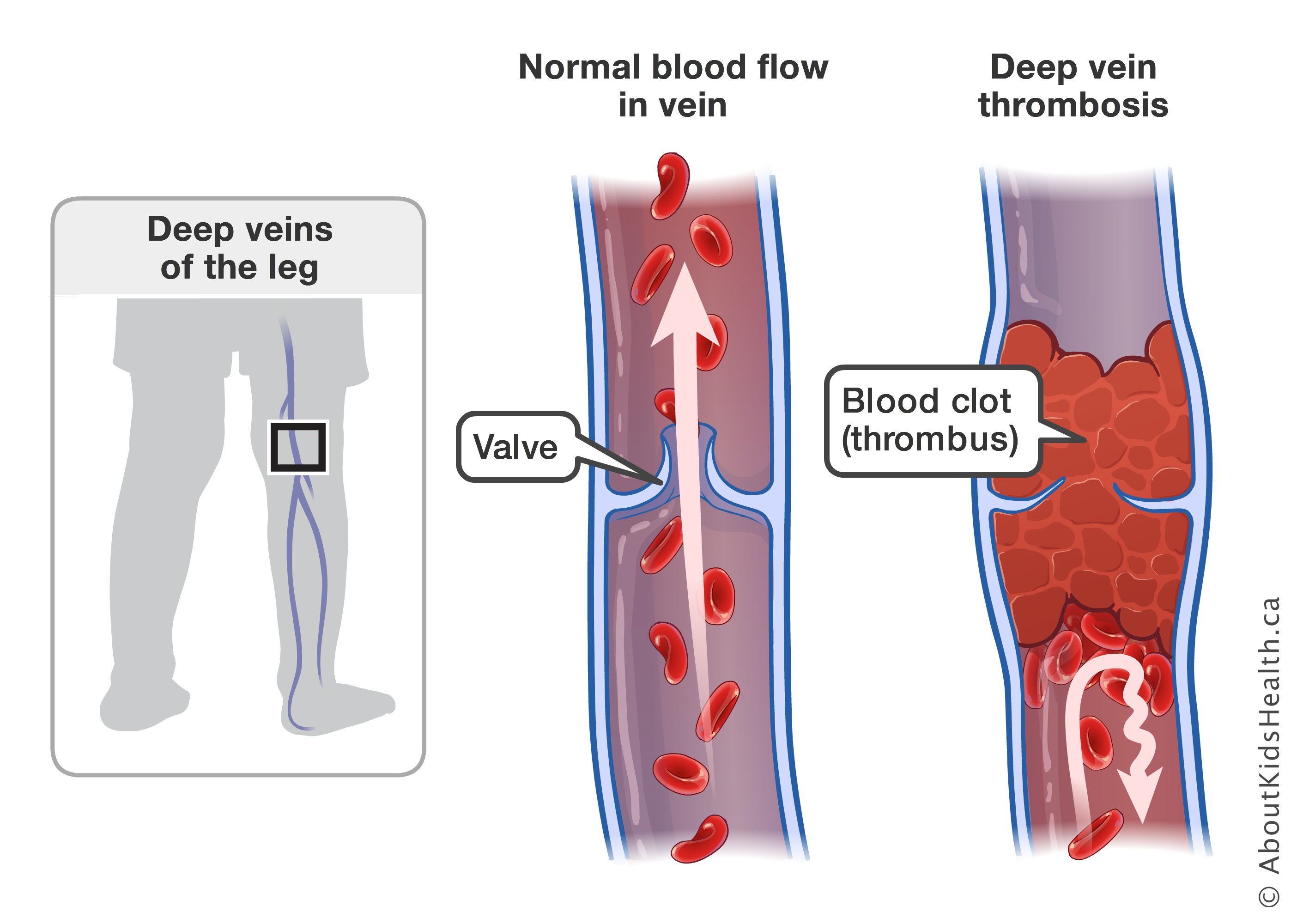
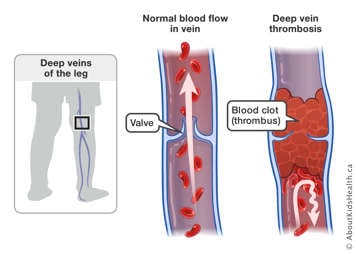
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in the deep veins of the arms or legs. Signs and symptoms of DVT include:
- Pain
- Limb swelling
- Redness
- Warmth
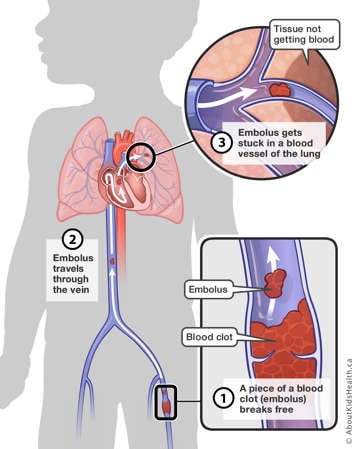
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blood clot that has broken off from a larger blood clot and travelled to the lung. Signs and symptoms of PE include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Blood while coughing
- Fainting
What are the signs and symptoms of prothrombin gene mutation?
A prothrombin gene mutation can be inherited from one or both parents. The type of prothrombin gene mutation a person has depends on whether they inherited one gene from one parent, or one gene from each parent.
Homozygous mutation
When a copy of the prothrombin gene mutation is inherited from one parent, and another copy of the prothrombin gene mutation is inherited from the other parent, this is called a homozygous mutation. It is very rare. The inheritance pattern is shown below:

Heterozygous mutation
When a mutated copy of the prothrombin gene is inherited from one parent, and another unaffected copy of the gene is inherited from the other parent, this is called a heterozygous mutation. This is the most common mutation and affects around 2% of the population. The inheritance patterns are shown below:


Risk factors of blood clots in people with prothrombin gene mutation
In people with heterozygous prothrombin gene mutation, the risk of thrombosis is increased 3-4 times. It is not known how much the risk increases in people with homozygous mutation. However, it is important to stress that the incidence of blood clots in children, in the general population, is quite rare, occurring at 0.07–0.14 per 10,000 children. As a person ages, their chance of developing a blood clot increases. The figure below shows the increasing frequency of blood clots with age.

How is the prothrombin mutation diagnosed?
To diagnose prothrombin gene mutation, a blood sample is taken for genetic testing.
How is prothrombin gene mutation managed?
There is no direct treatment for prothrombin gene mutation. Instead, the goal of management is to decrease the chance of getting blood clots in the first place. Additional risk factors for developing blood clots include:
- Obesity
- Immobility
- Cancer and chemotherapy
- Surgery or trauma
- Dehydration
- Catheters
- Pregnancy
- Use of oral contraceptives or hormone therapies
- Smoking
The following measures may be taken to prevent blood clots:
- Maintain a healthy diet. Talk to your child’s health-care team before changing your child’s diet and follow Canada’s Food Guide. Any irregular weight gain can contribute to the poor circulation of blood in the veins, increasing the risk of blood clots.
- Smoking and binge drinking or excessive alcohol consumption should be avoided.
- When travelling, encourage your child to walk around whenever possible. Decreased circulation of blood flow can increase the risk for blood clots.
- Encourage your child to get regular physical activity. Children and youth typically need at least 60 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous intensity physical activity every day.
- If a child with prothrombin gene mutation needs to take hormonal therapy (e.g., birth controls pills), talk to a gynecologist or pharmacist about how they can be safely taken, in order to help reduce the risk of blood clots.
When to seek medical attention
If you suspect your child has developed a blood clot, call their doctor immediately. If you cannot reach the doctor, take your child to the nearest emergency department.
At SickKids
Resources
For more information on thrombophilia, thrombosis, post-thrombotic syndrome and the management of these conditions, please visit the Thrombosis Learning Hub.
References
RH White. The Epidemiology of Venous Thromboembolism.
Circulation. 2003;107:I-4-I-8