With pulmonary stenosis, the pulmonary valve is unable to open completely, so the blood flowing from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery is constricted. "Stenosis" refers to the narrowing of a passageway. The constriction means that it is difficult for the right ventricle to pump the blood through the narrowing.
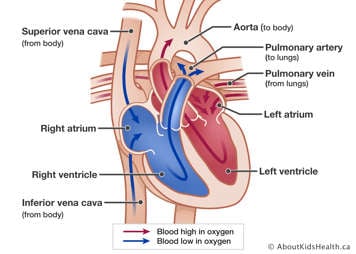
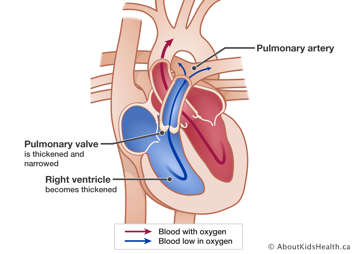
Pulmonary stenosis has been found in 8% to 10% of patients with congenital heart disease.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary stenosis?
In cases with severe narrowing, children may develop cyanosis and congestive heart failure. Babies who have this defect often show no symptoms, but will have a heart murmur.
An electrocardiogram, an echocardiogram, and a chest X-ray may be done to diagnose the condition.
How is pulmonary stenosis treated?
Balloon dilation valvuloplasty may be done to widen the opening. This is a cardiac catheterization procedure that stretches open the valve.
Children with more severe symptoms may need to undergo a surgical pulmonary valvotomy. With this procedure, the valve is surgically widened, often with the use of a patch.
