Diabetes can lead to health complications later in life if it is not properly managed. Complications are unwanted outcomes from an illness. There are various complications from diabetes that occur more often with high blood glucose levels and/or high blood pressure levels that are left untreated. Not everyone with diabetes will develop the complications seen below.
What are the potential complications of diabetes?
Complications fall into two groups:
- Microvascular complications involve small blood vessels.
- Macrovascular complications involve large blood vessels.
The risk of these complications can be improved with proper blood sugar (glucose) control and healthy lifestyle changes.
There are also other conditions that occur more often in people with diabetes and can develop over time.
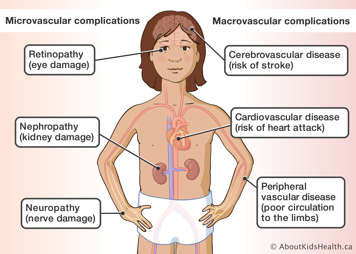
Microvascular (small blood vessel) complications
Microvascular complications occur mostly in people with diabetes. They include:
- retinopathy (eye damage), cataracts (clouding of the eye’s natural lens) or glaucoma (damage to the eye nerve)
- nephropathy (kidney damage; kidneys are the organs of the body that remove bodily waste in the urine)
- neuropathy (nerve damage; nerves are fibers that carry electric messages and allow communication between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body).
These problems almost never happen in young children and they are uncommon in teenagers. However, diabetes probably starts to have an effect from the time it begins.
Macrovascular (large blood vessel) complications
Macrovascular complications also occur in the general population, but they are more common in people with diabetes. They include:
- risk of heart attack (cardiovascular disease)
- risk of stroke (cerebrovascular disease)
- poor circulation to the limbs, which may also cause foot problems (peripheral vascular disease).
Macrovascular complications almost never happen to children or teenagers.
Risk factors for complications
A person’s risk of having complications is higher in the following situations. Many of these conditions are checked frequently in people with diabetes.
Poor blood sugar control
Optimal blood sugar control reduces the chance that complications will develop. However, that does not mean that someone with poor control will definitely have complications. It also does not mean that someone with excellent control is guaranteed to be complication-free.
Smoking
Smoking increases the risk of complications a great deal. Smokers with diabetes are at much greater risk of developing complications than non-smokers. Those complications will also worsen more quickly in people who smoke than in non-smokers. Quitting at any time is beneficial.
Unhealthy weight
People who are overweight have a greater risk of complications. Healthy eating and an active lifestyle reduce the risk and should be encouraged in everyone.
High blood pressure
High blood pressure (hypertension) increases the risk of complications for people with diabetes because of increased pressure on the kidneys, heart and blood vessels. Lowering the blood pressure with medical treatment and a healthy lifestyle reduces this risk. Regular blood pressure checks in clinic are an important part of diabetes care.
High blood fats
People with diabetes may develop high blood fat levels (hyperlipidemia). Blood fats are called lipids and include cholesterol and triglycerides. Following a healthy lifestyle, keeping a healthy weight, and keeping blood sugar levels in target range, can help keep blood fat levels in the normal range.
Having proteins in the urine
The kidneys filter the blood and get rid of the waste. Proteinuria is a condition where proteins leak into the urine instead of staying in the body. Finding these proteins in urine may indicate kidney problems.
Having diabetes for a longer time
Complications rarely arise in people who have had type 1 diabetes for less than five years and before puberty. In type 2 diabetes, complications may occur by the time of diagnosis. The longer a person has had diabetes (either type 1 or 2), the more likely complications are to appear.